Energy Equation
Energy Equation in Fluid Mechanics
The energy equation in fluid mechanics is a fundamental principle that describes the conservation of energy in a fluid system. It accounts for the different forms of energy present in a fluid, including kinetic energy, potential energy, internal energy (due to temperature), and the energy exchanged with the surroundings.
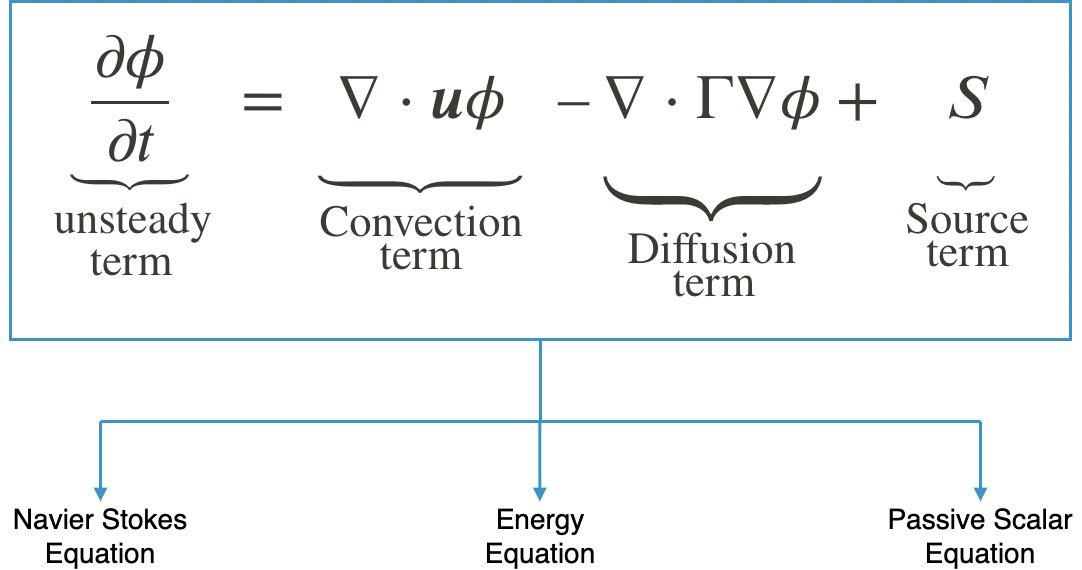
Key Components of the Energy Equation
Kinetic Energy:
- This is the energy associated with the motion of the fluid particles.
Potential Energy:
- This energy is due to the position of the fluid in a gravitational field.
Internal Energy:
- Internal energy is related to the temperature of the fluid.
Heat Transfer:
- Heat can be added or removed from the fluid, affecting its internal energy.
Work Done by the Fluid:
- Work can be done by or on the fluid due to pressure forces.
Dissipation Function:
- This term accounts for the irreversible conversion of mechanical energy into thermal energy due to viscous effects within the fluid. The dissipation function, often denoted by Phi, represents the energy lost as heat due to internal friction when fluid particles move relative to each other.
Dissipation Function Phi
The dissipation function quantifies the energy lost due to viscous effects. When fluid particles move relative to one another, frictional forces within the fluid generate heat, dissipating mechanical energy. This energy loss is particularly significant in high-viscosity fluids or turbulent flows. The dissipation function is usually complex and depends on the velocity gradients and viscosity of the fluid.
Application of the Energy Equation
Engineering Design:
- The energy equation is essential in the design and analysis of fluid systems, such as pipelines, pumps, turbines, and heat exchangers. Engineers use it to ensure that the energy input, conversion, and losses in the system are balanced for efficient operation.
Turbulence Modeling:
- In turbulent flows, the dissipation function becomes crucial for accurately predicting how energy is distributed between different scales of motion and how it ultimately converts into heat.
Environmental Studies:
- The energy equation helps in understanding natural phenomena such as atmospheric circulation, ocean currents, and weather patterns by accounting for the transfer of energy within these large-scale fluid systems.
Conclusion
The energy equation in fluid mechanics is a powerful tool that links the different forms of energy in a fluid system, considering both mechanical and thermal aspects. By incorporating the dissipation function and heat transfer terms, it provides a comprehensive view of how energy is conserved, transformed, and dissipated within a fluid flow. This equation is central to both theoretical studies and practical applications, making it indispensable in the field of fluid mechanics.