Grids
Structured Grids:
- Advantages:
- Simplicity: Structured grids are straightforward to implement and are logically similar to Cartesian grids.
- Connectivity: Each grid point has a fixed number of neighbors, simplifying programming.
- Efficient Solvers: The algebraic equation system has a regular structure, which allows for efficient numerical solvers.

- Disadvantages:
- Limited Flexibility: Structured grids can only be used for simple geometries, making them less suitable for complex domains.
- Grid Point Distribution: It’s hard to concentrate grid points in specific regions without creating very small or thin cells in other areas, leading to inefficient use of computational resources.
Block-Structured Grids:
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Allows for dividing the domain into blocks, each with its structured grid, making it suitable for more complex geometries.
- Local Refinement: Grids can be refined block-wise, improving resolution in specific regions without affecting the entire domain.
- Parallel Solving: Solvers can be applied block-wise, making it easier to handle complex flow domains.
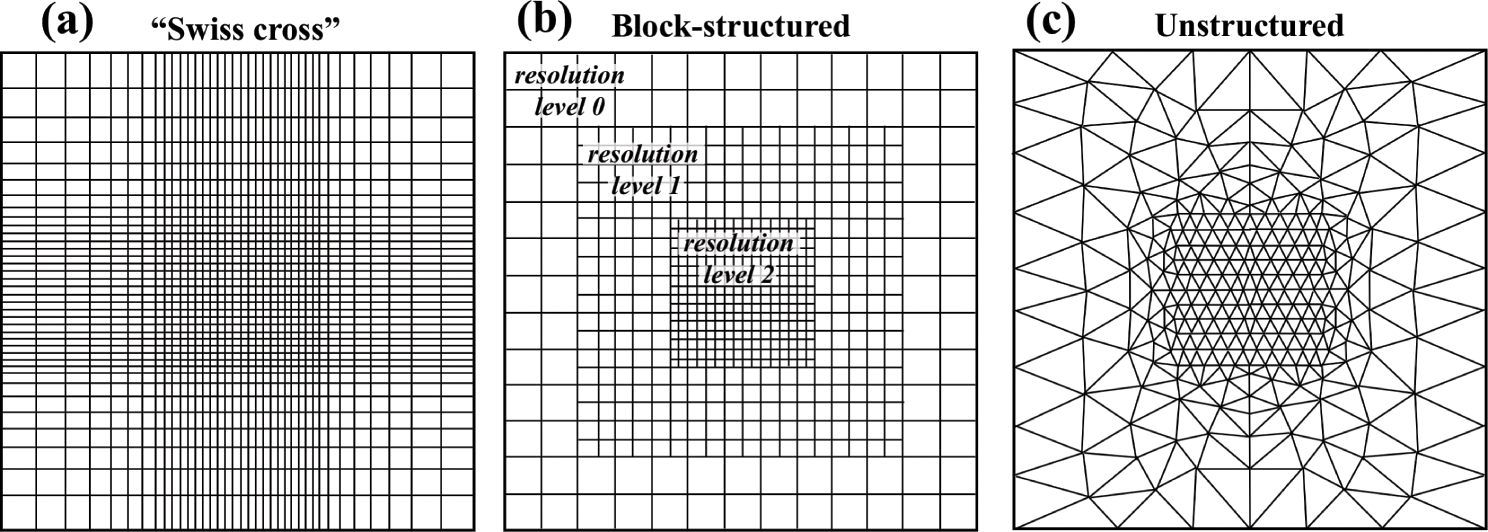
Disadvantages:
- Complex Programming: More challenging to implement than structured grids, especially at block interfaces.
- Conservation Issues: Ensuring conservation at block boundaries, especially with overlapping blocks, can be difficult.
Unstructured Grids:
Advantages:
- Maximum Flexibility: Can fit arbitrary and complex geometries, making them highly versatile.
- Automatic Generation: Grids can be generated automatically, and local refinement is easy.
- Adaptive to Finite Volume and Finite Element Methods: Unstructured grids work well with these methods, making them useful for a wide range of CFD problems.
Disadvantages:
- Complex Data Structure: Requires explicit specification of node locations and neighbor connections, making programming more complex.
- Irregular Equation System: The irregular structure of the grid leads to slower solvers, as the algebraic equation system lacks a regular pattern.
- Pre-Processing: Grid generation and pre-processing are more challenging compared to structured grids.
Impact on Accuracy and Efficiency:
- Structured Grids: Provide good accuracy and efficiency for simple geometries but struggle with complex domains.
- Block-Structured Grids: Offer a good balance between flexibility and efficiency, especially for moderately complex geometries.
- Unstructured Grids: Provide the best flexibility for complex geometries but can be less efficient due to irregular data structures and slower solvers.
Choosing the right grid depends on the problem’s geometry and the desired balance between accuracy and computational efficiency.